Proteins Food Group
All foods made from meat, poultry, seafood, beans and peas, eggs, processed soy products, nuts, and seeds are considered part of the Protein Foods Group. Beans and peas are also part of the Vegetable Group. Most people in North America eat enough food from this group, but need to make leaner and more varied selections of these foods.
Protein foods are broken down into parts called amino acids during digestion. The human body needs a number of amino acids in large enough amounts to maintain good health. You need to get enough dietary protein every day, because your body doesn't store it the way it stores fats or carbohydrates.
The amount of protein you need in your diet will depend on your age, sex, health, and level of physical activity, which is basically based on your overall calorie needs. The daily recommended intake of protein for healthy adults is 10% to 35% of your total calorie needs. For example, a person on a 2000 calorie diet could eat 100 grams of protein, which would supply 20% of their total daily calories.
Of the 20 naturally occuring amino acids, the human body can synthesize all but nine essential amino acids. The nine essential acids that the human body does not synthesize are: histidine, isoleucine, leucine, lysine, methionine, phenylalanine, threonine, tryptophan, and valine.
Protein primarily promotes growth and maintenance of body tissue. Proteins function as building blocks for bones, muscles, cartilage, skin, and blood. They are also building blocks for enzymes, hormones, and vitamins. Proteins are one of three nutrients that provide calories (the others are fat and carbohydrates). However, when caloric intake falls, protein is broken down and converted into glucose. The loss of protein can impede growth and repair of tissue.
Related Topics:
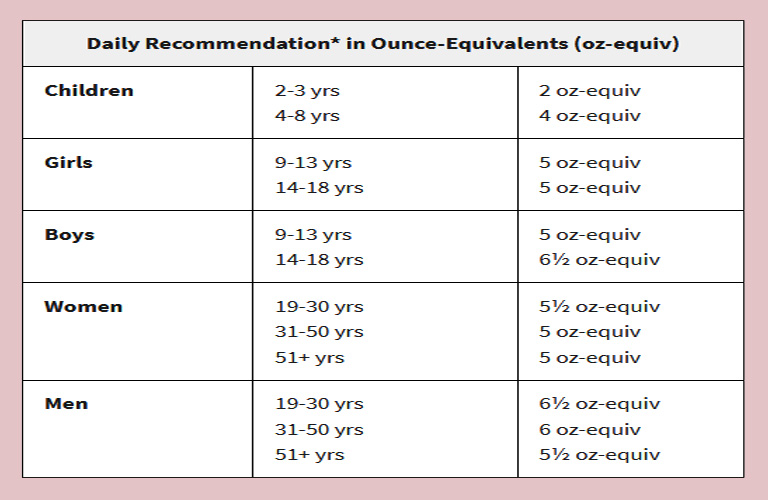
* These amounts are appropriate for individuals who get less than 30 minutes per day of moderate physical activity, beyond normal daily activities. The amount each person needs can vary between 2 and 6½ ounce-equivalents each day. Those who are more physically active may be able to consume more while staying within calorie needs.
For vegans, and those with limited access to animal-based food sources, and people who have significantly limited their meat, egg, and dairy product consumption, it is important to understand that essential amino acids can be obtained from incomplete protein sources, but this requires the daily selection of a variety of plant foods to ensure that all of the essential amino acids will be available for the body to synthesize its own proteins.
Select a variety of protein foods to improve nutrient intake and health benefits.
Did You Know?
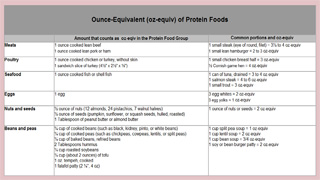
In general, 1 ounce of meat, poultry or fish, ¼ cup cooked beans, 1 egg, 1 tablespoon of peanut butter, or ½ ounce of nuts or seeds can be considered as 1 ounce-equivalent from the Protein Foods Group.Meat, poultry, fish, dry beans and peas, eggs, nuts, and seeds supply many nutrients. These include protein, B vitamins (niacin, thiamin, riboflavin, and B6), vitamin E, iron, zinc, and magnesium.
Protein is important for muscle growth and to repair body tissues. Protein can also be used by the body for energy, but only after carbohydrate stores have been used up.